With AI, machine learning, and big data initiatives driving change, financial institutions look to these technologies to optimize processes and improve customer experience.
But what are the technologies used in banking today? And which ones should financial institutions prioritize moving forward?
Data-driven decision making
Data has always been the major driving force in the decision-making processes, especially within the financial sector. But as the quality and amount of data available continue to increase, banks will start using advanced, topical analytics to make more accurate decisions.
Financial institutions will be able to use data for the following:
- Risk modeling – banks will be able to diagnose and predict potential risks earlier. As a result, financial experts can suggest solutions and workarounds to avoid these pitfalls.
- Fraud prevention – large swathes of data will help internal regulators at financial institutions monitor transactions to detect fraudulent activities.
- Customer satisfaction – personalized customer data will help banks improve the overall user experience across all platforms.
With new data management and analytics tools, financial institutions will be able to extend their data fabric as wide as possible to get the most accurate insights.
Process automation
As digital retail banking becomes the new norm, companies will find it easier to implement automation in their ecosystems. Robotic process automation (RPA) and digital process automation (DPA) will continue to grow as banks look for ways to eliminate redundancies and increase workflow efficiency.
Data from McKinsey also shows that IoT devices will surpass 50 million by 2025. Also, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning mean that over 50% of all internal banking processes can be automated.
Corporations like Capital One, Citi, and HSBC already use AI applications to run their digital retail banking operations. These financial giants also rely on AI-powered algorithms to authenticate customers’ identities.
Besides, deep learning and natural language processing algorithms can also help banks boost efficiency by automating repetitive, human-reliant tasks. The customer service sector in banking will use these technologies to assist customers in real-time and close cases faster.

Blending AI with RPA for better performance. Source: EPSoft
Better customer experience
Modern consumers crave personalized interactions with financial institutions when making payments, searching for information, or applying for loans. Regardless of the operation, users want to feel a special connection and enjoy a smooth user experience.
As competition for dominance continues to increase in the banking sector, companies like JP Morgan are paying more attention to features that make banking more convenient for customers. Whether it is contactless payments or investment solutions, financial organizations will always put customers first.
Customer support is another core aspect of the user experience in the banking sector. With 79% of Gen Z and Millenials looking to work only with financial institutions that cater to their personal needs, more banks will apply data science and AI to optimize the customer experience.
Increased focus on saving
The shock of the pandemic forced younger people to focus more on saving and investing. According to a Chase study, 40% of consumers are willing to explore more saving options to protect their money from unforeseen circumstances.
Besides, 91% of respondents to the Chase study admitted that autosaving technologies helped them cut down on their expenses and monitor their savings better.
To this effect, banks and financial houses are implementing AI-powered technologies to help customers automate their savings. A great implementation of this retail banking technology is the Chase Autosave feature, which allows users to do the following:
- Make daily savings manually.
- Save a specified percentage of every deposit.
- Choose an amount to save over a specific period.
Since most consumers rely on mobile banking services, companies will have to integrate autosaving features into future apps.
Open banking expansion
Open banking allows third parties to use another bank’s APIs. Instead of monopolizing these APIs without sharing them with other financial entities, banks can deliver them as services – banking as a service (BaaS).
With regulations like the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2), banks can explore BaaS models to monetize their tech innovations. These regulations ensure that the third parties using your bank’s API fall under these two categories:
- Account Information Service Provider (AISP) – analyzes customer account activity.
- Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISP) – make payments for the customer.
This open banking philosophy will continue to improve the quality of services that customers receive. Fintech and Insurtech companies can now take advantage of open APIs to help customers conduct transactions, buy medical and home insurance, and manage their finances.
Embedded financial services
Embedded financial services is a technology in retail banking that has now become part of everyday life. According to Accenture, embedded finance will reach a 230 billion USD valuation by 2025.How can banks and credit unions benefit from embedded financial services?
For starters, banks can use integrated services to keep consumers on their platforms. A Plaid survey shows that 76% of consumers will only increase their engagement with a digital banking service if it addresses their core problems.
Apart from that, non-financial companies like Amazon can also rely on embedded finance to offer loans to sellers based on predefined parameters. On average, such companies have increased engagement by 87.5% over the past five years.
Moving forward, this innovation will help small businesses process payments and loans faster. Financial institutions will also use embedded financial services to boost customer satisfaction, trust, and loyalty.
Decentralized finance
Decentralized finance is a relatively new retail banking technology, which explains why financial institutions are still reluctant to adopt this system. But with government regulators working on rules to guide transactions within this new framework, financial giants are already building early concepts for decentralized infrastructures.
JP Morgan’s Digital Investment Banking experts are currently developing a platform that implements blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. Over the coming years, more financial institutions will follow this model to decentralize their operations and adapt to evolving markets.
If DeFi becomes the new norm, banks will be able tolend money to customers without worrying about credit risks. Also, the transparency that DeFi platforms provide will decrease financial crimes such as fraud and theft.
Cloud integration
Around 90% of financial institutions use cloud services for some of their internal business processes. Most neobanks use a hybrid multicloud environment to secure company data on the cloud.
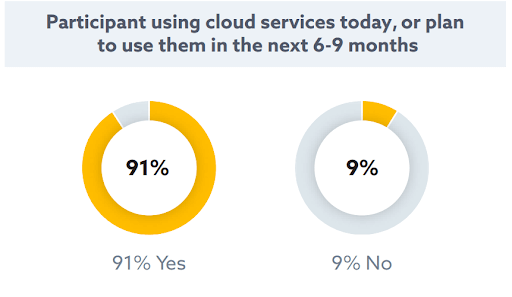
With the help of AI, data fabrics, BaaS, and BaaP (Banking as a Platform), banks can secure their workloads with more robust data protection infrastructures. Besides, cloud computing makes the banking infrastructure scalable, which allows institutions to adapt to market changes faster.
According to IBM, migrating a bank’s infrastructure to the cloud can only be successful depending on digital maturity, provider capability, and business case. Deloitte experts also predict that cloud banking will help synchronize collaborations within financial organizations by providing access to shared datasets.
Banking for sustainability
Climate change is a hot-button topic in every industry, and banking is not exempt. Nowadays, consumers expect banks to follow sustainable practices that mitigate the impacts of climate change.
In fact, 64% of young professionals say they won’t work for banks that don’t care about the environment. Owing to the potential financial costs of losing customers and employees to competitors, financial institutions are now embracing Green IT (Green Banking).
By moving their applications to the cloud, banks and financial organizations can reduce carbon emissions by 5.9% – which is around 6 million tonnes of CO2 every year.
Mergers with tech companies
The era of banks focusing solely on financial services is slowly fading into obscurity. As new technologies become available, banks and financial organizations will need to reinvent the existing models to provide better services to customers.
This reimagined digital ecosystem will unite corporations with non-banks to harness their combined access to resources and consumers.
For instance, Walmart is partnering with Ribbit Capital to “deliver tech-driven financial experiences tailored to Walmart’s customers and associates.” Going forward, such unions will become commonplace in the banking and consumer-goods retail sectors.
In addition, banks will have to function as full-scale tech (and Fintech) companies in order to stay competitive with juggernauts like Apple and Google. If more tech companies continue venturing into finance, traditional banks will need to merge or expand their scope of services to stay competitive.
Increased focus on security
According to CompTIA, financial institutions are most susceptible to cyberattacks, accounting for 23% of all cyberattacks over the last 18 months — an all-time high. Consequently, banks are doubling down on regulations and security protocols to protect personal and financial data from cyberattacks.

The cost of cybercrime in 2021
In the coming years, more banks will have to adopt AI tools to detect these attacks before they occur. Also, adopting robust cloud solutions from trusted providers will help branchless banks automate data security and enforce KYC and AML regulations.
Financial houses might also need to replace passwords with other convenient authentication protocols to boost security. Microsoft and Google have already set the standard with their stand-alone Authenticator apps, and other companies and financial institutions will follow in due time.
Conclusion
The future of retail banking technology will focus a lot on improving customer experience in contactless payments, data security, and retail services. In the coming months, banks will focus more on open banking solutions to provide better customer service, make data-driven decisions, and improve their workflow efficiency.
To get your finance business ready for future innovations and technological trends, SDK.finance offers white-label software to help you build a robust, scalable, future-proof, and user-friendly digital retail bank.