In the payments industry, success is defined not by design or marketing, but by how efficiently money moves through a system – how transactions are initiated, routed, settled, and reconciled. For FinTech founders aiming to launch a neobank, payment service provider (PSP), or any other money-movement product, understanding how payment rails work is essential. Behind every digital transaction lies a network of payment rails – the technological and regulatory infrastructure that determines how funds travel between accounts and institutions.
A payment processing network enables real-time, electronic transfer of funds between banks, supporting instantaneous transactions and broad adoption by financial institutions. These rails dictate which currencies can be supported, how quickly settlements occur, and which partners or networks a business can connect to.
This article explains payment rails as professionals in the field understand them – systematically, by technology type, geography, and business relevance. It shows how established rails such as ACH and SWIFT coexist with instant systems like FedNow and SEPA Instant, and how blockchain-based networks are redefining cross-border money movement. Choosing among different payment rails affects transaction speed, cost, and security, making it crucial to understand the options available for optimizing payment processing.
Payment rails meaning
A payment rail is the technological and regulatory infrastructure that enables money to move between accounts.
It defines how a payment instruction is transmitted, verified, cleared, and settled – and which financial institutions, processors, and intermediaries are authorised to participate in that process. During the payment process, payment rails facilitate the exchange of transaction details – such as payment instructions, account information, and funding specifics – between institutions to ensure secure and efficient execution and settlement of financial transactions.
In simple terms, payment rails are the transport routes of the financial system – the highways, airways, and shipping lanes that move value instead of physical goods.
Each has its own rules, speed, and cost:
-
ACH or SEPA function like domestic road networks – cost-effective but slower.
-
SWIFT operates as a global shipping route – reliable, but complex and time-consuming.
-
Blockchain rails resemble autonomous air corridors – decentralised, borderless, and continuously available.
Together, these rails form the backbone of money movement worldwide, ensuring that value can be transmitted securely between accounts, currencies, and countries.
How payment rails work?
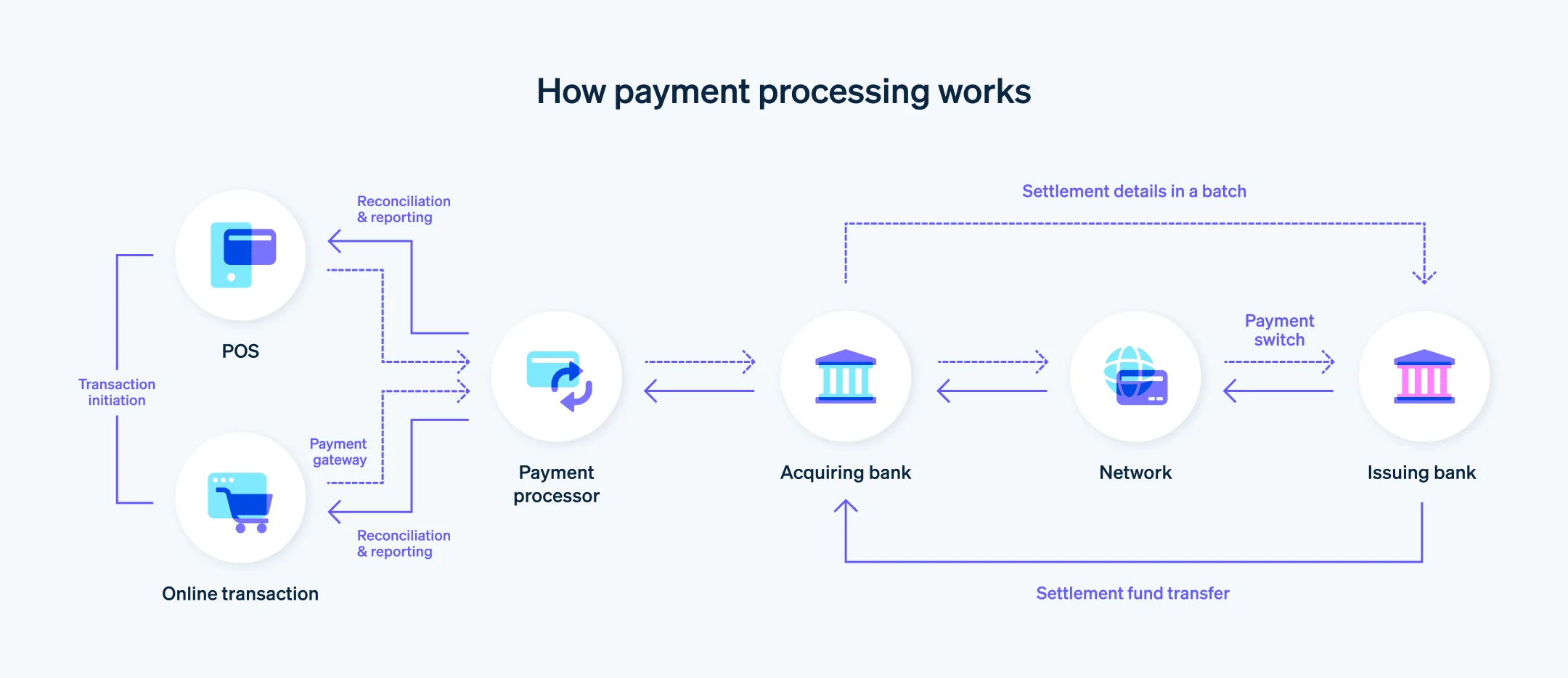
No matter the type, all payment rails follow the same fundamental process:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Initiation | The payer authorises a transaction through a bank, app, or merchant system. The payer’s bank initiates or authorizes the transaction. |
| 2. Transmission | Payment instructions travel through the selected rail. |
| 3. Clearing | Intermediary systems validate data and prepare balances for settlement. The sender’s bank validates the transaction before settlement. |
| 4. Settlement | Funds move between financial institutions, often through central banks or clearing houses. The recipient’s bank receives payment notifications and posts the funds. This process involves a funds transfer between banks, and payment rails facilitate the transfer of funds between financial institutions. |
| 5. Reconciliation | Both ledgers update, finalising the transaction. |
The main types of payment rails
FinTech founders should view payment rails as three evolutionary layers – traditional, modern, and emerging – each representing a different balance of reach, cost, and transaction speed. Participating financial institutions are authorized to access and utilize specific payment rails, enabling secure and efficient transactions within these systems. Understanding where your product fits within these layers helps you choose the right technology stack, partner banks, and compliance framework.
Traditional payment rails
These rails form the foundation of the modern financial system. They handle the bulk of global payment volume and are operated primarily by regulated financial institutions and clearing networks.
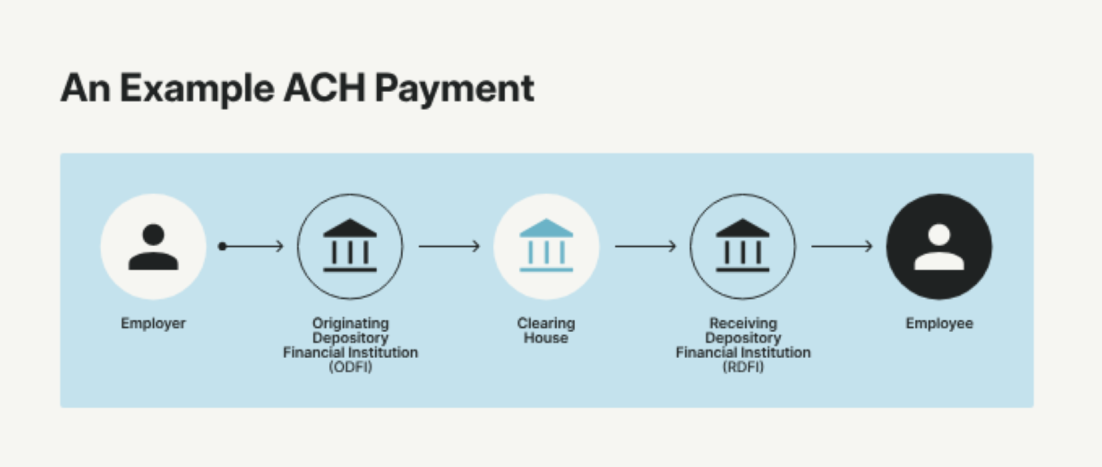
ACH (Automated Clearing House) – United States
ACH is a batch-based electronic payment system for bank-to-bank transfers, used for ACH payments including direct deposit, bill payments, and automated transactions. Used mainly for payroll, bill payments, and recurring debits, it processes transactions in scheduled batches – typically settling within 1-3 days.
Example: Most US employers use ACH direct deposits for wages, and services like PayPal rely on ACH to move funds between user accounts and banks. ACH is optimized for low value transactions such as bill payments and payroll. A typical ACH transaction involves the originating bank sending payment instructions to the ACH operator, which then routes the funds to the receiving bank for final settlement.
SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) – Europe
SEPA harmonises euro-denominated payments across 36 countries, making cross-border transfers as simple as local ones. SEPA supports both credit transfers and direct debit transactions, providing a unified framework for electronic euro payments. It enables transfers from one bank account to another across participating countries, streamlining financial operations. It supports both standard and instant transfers, with SEPA Instant delivering payments in under 10 seconds. In a typical SEPA transaction, both the sender and recipient banks play key roles in processing the payment using the relevant bank account details.
Example: FinTechs like Revolut and Wise use SEPA to let users send and receive euros across Europe without extra fees.
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) – Global
SWIFT is a global messaging network and secure communication platform used by financial institutions for international wire transfers. It doesn’t move money itself – it transmits payment instructions, account details, and transaction details securely between banks, often through intermediaries, to facilitate and process international wire transfers. Example: Wise built a network of local bank accounts to avoid SWIFT’s slow and expensive routes, allowing faster and cheaper cross-border transfers.
Card Networks (Visa, Mastercard, Amex)
Card networks act as intermediaries that facilitate payment transactions between issuing banks (which sponsor the card for the customer) and acquiring banks (which process card payments on behalf of merchants). These networks establish the rules for authorization, transaction routing, and settlement of credit and debit card payments, supporting both online and point of sale system transactions. The issuing bank is responsible for authorizing transactions and providing cards to customers, while the acquiring bank handles merchant payment processing and settlement within the card network infrastructure. Card networks make card payments possible both online and in-store, processing billions of transactions yearly, including those made with debit cards.
Example: Processors like Stripe and Marqeta rely on Visa and Mastercard rails to enable global card acceptance for businesses.
SDK.finance provides pre-built modules and APIs for connecting to these traditional payment networks – enabling fintech products to plug into ACH, SEPA, SWIFT, and card schemes within a single ledger-driven system.
Wire Transfers
Wire transfers are a widely used payment rail for moving funds directly between bank accounts, especially when speed and reliability are critical. This payment method is often chosen for high-value or time-sensitive transactions, such as real estate closings, business-to-business payments, or urgent cross border transactions. The process begins with the originating depository financial institution (ODFI), which validates the payment request, checks for sufficient funds in the sender’s account, and then initiates the transfer. The payment instructions are securely transmitted – often via the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) for international transfers, or through the Federal Reserve’s Fedwire system for domestic U.S. payments.
Once the payment message is sent, the receiving depository financial institutions (RDFI) process the incoming funds and credit the recipient’s bank account. Wire transfers are considered a secure and efficient payment method, as they involve direct communication between financial institutions and typically settle on the same day, or even within minutes for some domestic wires.
However, this speed and security come at a cost: transaction fees for wire transfers can range from $10 to $50 or more, depending on the financial institution and whether the transfer is domestic or international. Despite the higher transaction fees, wire transfers remain a preferred choice for transferring large sums or when immediate availability of funds is required.
Credit Unions and Payment Systems
Credit unions are an integral part of the payment systems landscape, providing their members with a comprehensive suite of payment services. By participating in payment processing networks such as the Automated Clearing House (ACH) network, credit unions enable seamless ACH transactions, including direct deposits, bill payments, and recurring payments between members and other financial institutions. Many credit unions also offer debit card payments, online transactions, and real time payment options, such as wire transfers or instant person-to-person payments, to enhance member convenience.
To stay competitive with larger banks, credit unions often collaborate with third party service providers to deliver innovative solutions like mobile payment apps and digital wallets. These partnerships allow credit unions to offer secure, efficient, and user-friendly payment options, ensuring their members have access to the latest payment technologies. By leveraging robust payment systems and the ACH network, credit unions can process a wide range of financial transactions, maintain strong relationships with their members, and uphold their reputation for personalized service in an increasingly digital payments market.
Modern payment rails
Modern rails emerged to overcome the limitations of batch processing, focusing on real-time availability, transparency, and open connectivity. A payment processor plays a crucial role in facilitating, securing, and managing transactions across these modern payment rails, ensuring efficient and safe movement of funds.
Real-Time Payment Systems (Faster Payments, FedNow, UPI, Pix)
These infrastructures enable real time payments, allowing instant, 24/7 transfers and eliminating the delays of traditional settlement cycles. Real time payments, such as those processed through the Faster Payments Service (UK), provide near-instant domestic transfers since 2008. The Faster Payments Service is a UK-based system that facilitates real-time, near-instantaneous electronic transfers between banks and financial institutions, operating 24/7 for domestic, low-value transactions.
- Faster Payments (UK): Enables near-instant domestic transfers since 2008 through a dedicated faster payments service.
- FedNow (US): The Federal Reserve’s 2023 initiative for real-time interbank payments, supporting use cases like loan disbursements and immediate settlements.
- UPI (India): Processes billions of mobile payments monthly between banks, improving cash flow for businesses and individuals.
- Pix (Brazil): Central bank-led instant rail supporting 24/7 payments and facilitating rapid loan disbursements.
In these systems, the payer’s bank plays a critical role by initiating and authorizing the transaction, confirming sufficient funds, and communicating with the recipient’s bank to complete the payment.
Example: Businesses use FedNow for immediate supplier settlements and loan disbursements, while apps like Google Pay in India leverage UPI to enable real-time peer-to-peer payments, all of which help improve cash flow.
Open Banking APIs
Open banking introduces programmable access to financial accounts, letting third-party apps initiate payments and retrieve account data directly with user consent. Open banking APIs enable account to account (A2A) payments, allowing funds to move directly between users’ bank accounts without intermediaries. These APIs often rely on real-time rails beneath them (like Faster Payments or SEPA Instant). Example: Providers like TrueLayer, Plaid, and Tink aggregate bank connections under one API. Even legacy processors like Worldpay now use open-banking APIs to offer “Pay by Bank” options with lower fees than card payments.
Emerging payment rails
Emerging rails use decentralised technology to create borderless, always-on, programmable payment networks. These emerging payment rails also include digital currencies such as cryptocurrencies, which operate on blockchain technology and serve as decentralized, digital payment methods for both everyday transactions and investments.
Blockchain Networks (Bitcoin, Ethereum, Stellar)
Blockchain-based rails rely on distributed ledgers instead of central clearing houses. Blockchain networks maintain secure, immutable transaction records on a decentralized ledger, ensuring that all transactions are transparently verified and cannot be tampered with. They allow peer-to-peer value transfer globally without intermediaries – useful for cross-border transactions and settlements.
Example: Payment processors like BitPay and Coinbase Commerce let merchants accept cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ether, converting them instantly to fiat.
Stablecoins (USDC, USDT, PYUSD)
Stablecoins are blockchain-based assets pegged to fiat currencies, combining crypto speed with traditional stability.
They enable instant, low-cost global transfers – 24/7.
Example: USDC by Circle allows businesses to send digital dollars across borders in seconds, redeemable 1:1 for USD.
Bitcoin Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a second-layer protocol built on Bitcoin that enables microtransactions at near-zero cost by processing them off-chain before settling on the Bitcoin network.
Example: The FinTech app Strike uses Lightning for cross-border remittances, sending BTC instantly and converting it to local currency on arrival.
SDK.finance supports hybrid use cases by offering a multi-asset ledger that records fiat, crypto, and tokenised transactions within a unified accounting environment – making it easier for FinTechs to experiment with or adopt blockchain-based payment rails alongside traditional ones.
Traditional rails provide reliability and regulatory certainty, modern rails bring speed and openness, and emerging rails enable 24/7 programmability.
Everything you need to launch crypto wallets, payments, and custody
Learn morePayment rails examples
| Example | Rail Used | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Payroll deposits (US) | ACH | Employers send direct deposits in bulk. |
| Instant domestic transfers (UK) | Faster Payments | Bank-to-bank transfers in seconds. |
| E-commerce transactions | Visa / Mastercard | Instant authorisation for online purchases; a form of online payments facilitated by card networks. |
| Cross-border supplier payment | SWIFT + SEPA | Message via SWIFT, settlement through SEPA. |
| Wallet top-ups | ACH / SEPA Instant / RTP | Wallet apps fund or withdraw through connected rails. |
| Crypto-to-fiat remittance | Blockchain + Bank Rail | Stablecoins transferred via blockchain and cashed out through SEPA or ACH. |
Comparing the rails
| Rail | Speed | Cost | Reach | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACH | 1-3 days | Low | US | Payroll, bills |
| SEPA | 1 day / instant | Low | EU | Euro transfers |
| SWIFT | 1-3 days | High | Global | Cross-border |
| Card Networks | Seconds / 1-2 days | Medium-High | Global | Consumer payments |
| RTP / FedNow | Seconds | Low-Medium | Domestic | Instant transfers |
| Open Banking | Seconds-minutes | Low | EU, UK | A2A e-commerce |
| Blockchain | Seconds-minutes | Variable | Global | Remittances, settlement |
Note: Transaction costs can vary significantly across these payment rails. Understanding transaction costs is crucial for selecting the most efficient and cost-effective payment method for your needs.
What is a multi-rail payments strategy?
A multi-rail strategy combines several payment networks to achieve resilience, cost efficiency, and flexibility.
Instead of depending on one rail (e.g. SWIFT or ACH), businesses dynamically route transactions across multiple options based on cost, geography, and transaction size.
Benefits:
- Redundancy: Avoids downtime if one network fails.
- Cost optimisation: Routes via the lowest-cost option.
- Speed flexibility: Prioritises instant rails for urgent transfers.
- Scalability: Expands geographic coverage without changing systems.
SDK.finance‘s modular ledger and API gateway make multi-rail orchestration possible – allowing instant switching between rails within one consistent backend.
Dynamic routing: the future of payment rails
The next evolution is dynamic routing – intelligent, automated rail selection in real time.
Routing engines assess parameters like transaction cost, liquidity, currency, and network speed, then automatically pick the most efficient rail for each payment.
This allows FinTechs to move funds optimally – whether via ACH, RTP, SEPA, or blockchain – without manual intervention.
Which payment rails are right for your business?
| Business Type | Recommended Rails | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Bank | SEPA, ACH, RTP, Card | Full retail capabilities. |
| PSP | Card + ACH / SEPA Instant | Acceptance + settlement coverage. |
| Remittance Service | SWIFT, SEPA, Stablecoins | Global reach with cost control. |
| Gig Platform / Marketplace | RTP, FedNow | Instant payouts. |
| Crypto-FinTech | Blockchain + ACH / SEPA | Hybrid crypto-fiat model. |
| B2B Enterprise Platform | SWIFT, SEPA, Open Banking | High-value and recurring payments. |
SDK.finance helps each segment design a rail mix that fits its regulatory and business model, providing one API-ready backend to manage them all.
Challenges of connecting to payment rails
To operate on payment rails, a company must cover two essential layers – the business setup and the technology foundation:
1. Business setup
To gain access to payment rails, your organisation must:
- Open active payment accounts with licensed financial institutions.
- Complete KYC, KYB, and AML onboarding with each financial or banking service provider involved in your product.
- Sign direct agreements with these vendors, providing corporate registration documents, financial statements, and ownership details.
Once onboarding is complete and your company receives account credentials from partners, it becomes authorised to access the selected payment rails.
2. Technology foundation
The next step is ensuring your system can connect to those rails and process transactions properly. This is often the most complex part because:
- Each rail follows its own messaging standards (e.g. ISO 8583, ISO 20022).
- Certification and testing requirements vary between providers.
- Settlement and reconciliation cycles differ across rails and currencies.
- Continuous compliance and security monitoring are required.
Building and maintaining such integrations in-house can take months and requires specialised engineering and compliance resources.
Why ready-to-go software makes sense:
- It removes the need to build and certify every integration manually.
- It reduces time-to-market by using pre-tested, pre-integrated modules.
- It minimises compliance and operational risks by relying on proven infrastructure.
SDK.finance, a leading core payment software provider, delivers all this out of the box – offering a real-time ledger engine and 470+ APIs already connected to major banks, processors, and payment rails.
The platform complies with the industry’s highest security and regulatory standards, including PCI DSS Level 1 certification for secure card data processing and ISO 27001:2022 certification for information security management.
This allows FinTech teams to focus on business partnerships, licensing, and scaling, while SDK.finance provides the certified technological backbone that ensures funds move, settle, and reconcile accurately and securely across every connected rail.
Payment rail security
Payment rail security is fundamental to the integrity and trustworthiness of the payment processing ecosystem. Whether funds are moving through the ACH network, card networks, or other payment rails, financial institutions and payment service providers must implement advanced security measures to ensure the secure and efficient movement of money. This includes deploying encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive payment information, such as credit or debit card details, during transmission and storage. Multi-factor authentication and other secure authentication protocols are also essential to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of fraud.
Compliance with industry standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), is mandatory for any entity handling credit or debit card transactions. These regulations help safeguard payment information and maintain the overall security of the payment system. By prioritizing robust security practices, financial institutions and payment processors can protect their customers’ funds, reduce the risk of cyber threats, and foster confidence in digital payment methods.
Payment rail regulation
Payment rail regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability, security, and efficiency of the global payment processing ecosystem. Regulatory authorities, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States and the European Central Bank in the Eurozone, oversee the operation of major payment rails, including the ACH network and the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) payment system. These bodies establish rules and standards for payment processing, settlement, and security, ensuring that payment systems operate reliably and transparently.
Regulation of payment rails is designed to promote competition, encourage innovation, and protect consumers within the payments market. By enforcing strict guidelines, regulators help prevent fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities that could compromise the integrity of the financial system. Ultimately, effective payment rail regulation ensures that payment service providers and financial institutions act in the best interests of their customers, while supporting the secure and efficient movement of funds across domestic and international payment systems.
The future of payment rails
Three trends are reshaping the landscape:
- Interoperability – unified messaging under ISO 20022.
- Always-on settlement – real-time becomes standard.
- Programmable money – smart contracts automate financial logic.
SDK.finance’s flexible, modular platform is already built to accommodate these developments, ensuring future-proof payment connectivity.
SDK.finance: your bridge to global payment rails
SDK.finance acts as the technological backbone connecting FinTechs, banks, and PSPs to global payment rails through one system.
Key Platform features:
- Real-time ledger core.
- 60+ functional modules (accounts, KYC, AML, reconciliation).
- Pre-integrated payment rails
- 470+ APIs for connecting banks and processors.
- PCI DSS Level 1 and ISO 27001 certified.
- Source code and SaaS models.
You don’t need to integrate each rail individually – SDK.finance delivers these capabilities out of the box, allowing your team to focus on building products and managing operations while the platform powers transactions behind the scenes.
Conclusion
Payment rails form the circulatory system of modern finance. From ACH and SEPA to RTP, FedNow, and blockchain, they define how money moves through the global economy.
The right strategy blends these rails intelligently – a multi-rail, dynamically routed approach that balances cost, speed, and reach.
SDK.finance provides exactly that: a unified technological foundation that connects your business to every major payment rail, supports future ones, and ensures each transaction is processed accurately and in real time. In other words – SDK.finance delivers the technology so that your customers never need to think about the rails at all.