Nowadays, seamless and secure payment experiences are no longer a luxury – they’re a necessity. Due to their widespread acceptance, interoperability, and security features, open-loop payment systems have become essential for global commerce, allowing seamless transactions across platforms and merchants.
In this article, we’ll delve into the key features, benefits, and implementation steps to help you harness the power of open-loop payments for your business.
What are open-loop payments?
Empty
One of the most common examples of an open-loop payment system is credit and debit cards issued by major financial networks such as Visa and MasterCard.
Open loop payment systems vs. closed loop
Both open-loop and closed-loop payment systems have their unique advantages and disadvantages. The best choice for a business depends on its specific needs, goals, and target market. To assist in making an informed decision, let’s compare the key points of each system.
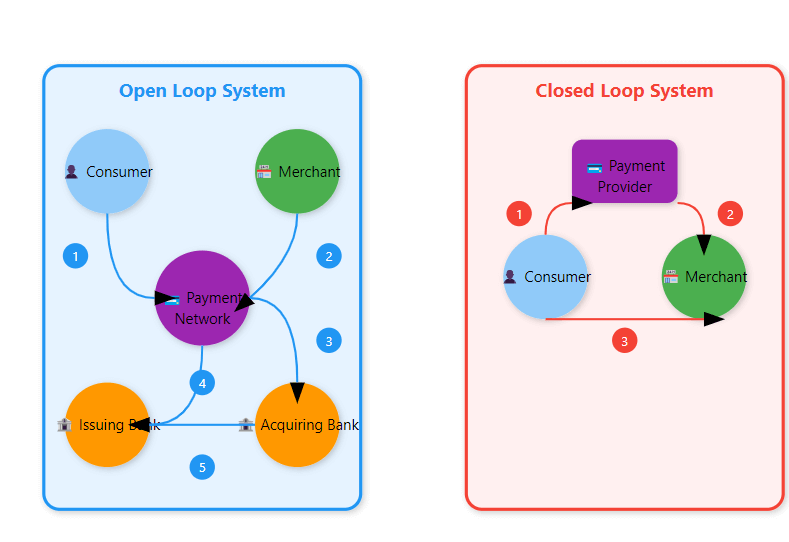
What is the difference between closed-loop and open-loop payment systems?
Open-loop payment systems involve several different parties: the consumer, merchant, issuing bank, acquiring bank, and payment network. These systems can be used at various merchants, like major credit card networks.
On the other hand, closed-loop payment systems are simpler and involve only the consumer, merchant, and a single payment provider. These systems are usually limited to specific merchants or a single company’s ecosystem.
| Feature | Open-loop payments | Closed-loop payments |
| Network scope | Transactions occur across various networks and merchants. | Transactions are limited to specific networks or merchants. |
| Card issuance | Utilizes standard bank-issued credit or debit cards. | Uses proprietary cards or apps exclusive to the network. |
| Merchant acceptance | Widely accepted by numerous merchants globally. | Restricted to designated merchants or service providers. |
| Transaction fees | Generally higher due to multiple intermediaries. | Typically lower due to fewer intermediaries involved. |
| Data control | Less control over consumer data; shared among entities. | More control over consumer data for targeted marketing. |
| Flexibility | Greater flexibility and convenience for consumers; can use the same card across various platforms. | Limited flexibility; can only be used within the issuer’s ecosystem. |
| Examples | Visa, Mastercard, American Express. | Starbucks mobile app, store-specific gift cards. |
Despite their differences, both open-loop and closed-loop payment systems can be beneficial for businesses in various ways.
When to use open-loop systems:
- Large-scale retail: Open loop systems are ideal for businesses with a wide customer base and a need for global acceptance, such as large retailers, supermarkets, and department stores.
- Travel: For travelers, open-loop systems offer the convenience of using a single payment method across different countries and regions, making them essential for international travel.
- International commerce: Businesses engaged in international trade can benefit from the global reach and acceptance of open-loop systems, which can help them expand their customer base and facilitate cross-border transactions.
Everything you need for a speedy and cost-effective start.
Learn moreWhen to use closed-loop systems:
- In-store loyalty programs: Closed loop systems can be used to create exclusive loyalty programs that reward customers with points or discounts for purchases made at specific stores or chains.
- Brand-specific initiatives: For businesses that want to promote their brand or specific products, closed-loop systems can be used to create targeted promotions or limited-time offers.
How do open-loop systems work?
When making a payment, customers can use a payment card (such as a debit or credit card) or a digital wallet at a store to pay for items or services.
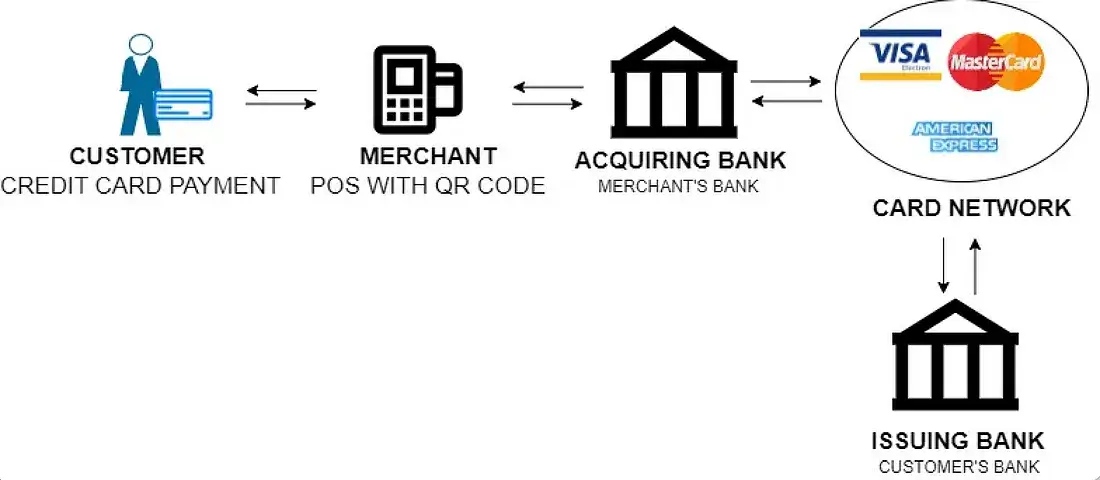
Here’s what happens during the payment process:
1. Payment initiation
Customers use a payment card (like a debit or credit card) or a digital wallet to pay for items or services at a store.
2. Transaction authorization
The store sends the payment request to the payment processor, which communicates with the card network (e.g., Visa, MasterCard). The network then seeks permission from your bank.
3. Checking the account
The bank verifies the user’s account to ensure there are sufficient funds or credit. If everything is in order, the purchase is approved, and the store receives an authorization code to proceed with the payment.
4. Paying the store
Once the purchase is approved, the money is transferred from the customer’s bank to the store’s bank through the card network. The duration of this transfer may vary based on the system’s regulations.
5. Completing the process
The store receives the payment in its account, minus any applicable fees, and the purchase is finalized.
Source: Medium
To support seamless integration with open-loop payment networks, SDK.finance Platform offers a suite of flexible APIs and pre-built solutions that simplify the connection to major card networks like Visa and MasterCard.
Benefits of open-loop payments for business
Wide acceptance and flexibility
Open-loop payment systems are accepted everywhere, making it easy for customers to use their cards or digital wallets at countless stores worldwide. This flexibility means you can use the same payment method in any store, anywhere.
For businesses, this means more customers and more sales. They aren’t limited by where their customers are or what technology they use. Global acceptance leads to happier customers and more spending because paying is so simple.
Imagine you’re traveling to a new country and want to buy a souvenir. You can use your Visa credit card at almost any store, from a small local shop to a large department store. This is because Visa is an open-loop payment system, accepted by a wide range of merchants worldwide.
Potential for the broader customer base
Businesses can attract more customers worldwide by offering open-loop payment methods. Customers appreciate the convenience of using one payment method instead of many, which can lead to increased customer loyalty and spending.
For example, a restaurant that accepts popular open-loop payment methods like Visa or Mastercard can attract customers from all over the world, not just locals.
No need for expensive infrastructure
One of the key advantages of open-loop systems is no need for expensive payment systems. With open-loop systems, businesses don’t have to build their own payment networks. They can use trusted ones like Visa or Mastercard. This saves them money and makes it easier to start accepting payments.
Industry examples of open-loop payments
Open-loop payment systems have become increasingly popular across various industries, offering businesses and consumers a multitude of benefits. Let’s explore some key examples where these systems have made a significant impact.
Retail
Big stores like Walmart and Target use open-loop systems to let customers pay with the cards they like. This means customers can use Visa, Mastercard, and other popular cards to pay, whether they’re shopping in-store or online.

Open-loop systems also work with contactless payments, making checkout faster and easier. This flexibility keeps customers happy and coming back, especially in busy places like supermarkets and big stores.
E-commerce
Online stores like Amazon and eBay use open-loop systems to make payments safe, easy, and convenient. These systems work with payment gateways to keep things secure and support payments in different currencies.
This helps businesses sell to customers all over the world without needing their own payment systems, which makes them grow faster and reach more people.
Travel and hospitality
Open-loop systems are important for travelers to make payments easily in different countries. Businesses like airlines, hotels, and car rental companies use these systems to accept payments from customers around the world.
Companies like Marriott and Expedia let travelers use their credit or debit cards, no matter where they are. This makes customers happier and helps them avoid problems with currency conversion and payments.
SDK.finance has enabled businesses across various industries to successfully implement open-loop payment systems, boosting their operational efficiency and customer reach.
7 Steps to implement open loop systems in your business
While integrating open-loop payment systems can seem complex, focusing on these key steps will ensure a smooth and successful implementation.
Step 1. Assess business needs
Evaluate your business requirements. Consider factors such as your target market, whether you operate locally or internationally, and the payment preferences of your customers. Understanding these will help you determine if an open-loop system is the right fit.
Step 2. Research payment providers
Identify potential payment network providers (such as Visa, MasterCard, or digital wallets like PayPal) and compare their offerings. Look for providers with a global reach, strong security protocols, and competitive fees that align with your business’s size and scale.
Step 3. Ensure compliance
Open-loop systems must comply with regulatory standards such as PCI DSS for secure payment processing. Make sure your systems meet all necessary legal and compliance requirements before implementing them.
Step 4. Select a payment gateway
Choose a payment gateway that seamlessly integrates with your existing systems and supports open-loop payment methods. Ensure it is capable of handling multiple currencies and can scale as your business grows.
Step 5. Choose the software provider
It’s essential to select a reliable software partner to help you implement and maintain your open-loop system. SDK.finance offers a powerful digital wallet software Platform that streamlines the integration of open-loop payment systems for your business.
The SDK.finance FinTech Platform provides the following features for building your payment system:
-Seamless client onboarding
-Accounts in any currency
-Streamlined transactions
-Currency exchange
-User action history
-Contracts and vendor management
-Flexible fees and limits configuration
The solution comes with pre-integrated providers for key functions such as payment acceptance, card issuance and KYC compliance, allowing you to set up your financial transactions with ease.
The platform also has a robust workload capacity of 2700 TPS* (transactions per second), supporting your business growth.
Step 6. Test and optimize
Test all major functionalities: payment processing, account management, and transaction history. Verify everything operates as expected. Perform vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to detect and address potential security risks.
Step 7. Launch the product
Once the system is live, make sure to effectively communicate the launch of the new payment options across different channels. Provide customer support resources like FAQs, tutorials, or live chat to help users with any questions or issues.
Conclusion
Open-loop payment systems are transforming the way businesses and consumers transact, providing unprecedented flexibility, convenience, and global accessibility. SDK.finance offers a comprehensive solution specifically tailored to empower businesses for a seamless and efficient open-loop payment system implementation.


