As mobile devices become more popular, so does the prevalence of mobile payment apps. The convenience of paying for goods and services with a few taps on a smartphone screen has made mobile payments a popular option for consumers around the world. But as mobile payments take off, so does the risk of fraud and identity theft. That’s why it’s important that mobile apps are equipped with strong security technologies to protect your finances. In this article, I’ll go over the importance of security technologies in payment apps and the different types of security technologies that are commonly used.
Introduction to mobile payment apps
Mobile payment apps are software applications that allow users to make payments using their smartphones or other mobile devices. These apps are growing in popularity because they provide a convenient and easy way to pay for goods and services without the need for cash or credit cards. These software programs are used for a variety of purposes, including purchasing goods and services at brick-and-mortar stores, paying bills, and transferring money to friends and family.
Mobile wallets have not hit the mass consumer market just yet, and m-payments technology is still early in its days, according to its adoption rate. But a 210% growth forecast for this year is a good place to start. According to eMarketer, in the US alone the value of mobile payment transactions is expected to go up to $27 billion from $8 billion in 2015, reshaping the understanding of money transfers for both businesses and consumers.
Risks related to mobile payments
However, before m-payments reach the promised state of zen, barriers have to be knocked down, both technological and psychological. A Fed’s recent survey found out that 65 percent of consumers fail to see any benefit in using a mobile wallet. But is this the core of the problem?
With an increasing number of cyberattacks worldwide, security becomes one of the key concerns among mobile device users. And subsequently, this affects the m-payments adoption rate. A recent study has shown that 40 percent of consumers are concerned about cybersecurity, which stops them from connecting their credit card to a mobile device. At the same time, a total of 89 percent of users wouldn’t know if their mobile phone has been infected through a cyber attack, a study by the app security specialist Promon revealed. As a result, the security aspect of what is deemed to be a more secure way of transferring money is stalling the adoption of m-payment solutions.
Some of the most common security threats include:
- Phishing scams involve tricking users into revealing their financial information, such as their credit card number or bank account details. These scams can be carried out through emails, text messages, or other types of communications.
- Malware is a type of software that is designed to infiltrate your mobile device and steal your financial information. Malware can be spread through a variety of channels, including apps, emails, and text messages.
- Hacking attacks involve attempting to gain unauthorized access to your mobile payment app or financial information. Hackers can use a variety of techniques to carry out these attacks, including brute force attacks, social engineering, and other methods.
And while the complexity of malware used for identity fraud, merchant breaches, spyware and other types of cyberattacks is increasing, there are also numerous ways to protect mobile wallets and contactless payments. Below are the four most commonly-used ones.
Importance of security technologies solutions for mobile payment apps
Given the risks associated with mobile payments, it’s essential that mobile payment apps are equipped with strong security technologies to protect your finances. The main reasons why it is crucial to use mobile payment security solutions:
- Protect sensitive financial information. Mobile payment apps deal with sensitive financial information, such as credit card details, bank account numbers, and personal identification information. Security technologies such as encryption, tokenization, and biometric authentication are used to protect this information from being accessed by unauthorized parties
- Prevent fraud and cyberattacks. Mobile payment options are vulnerable to various types of fraud and cyberattacks, such as phishing, malware, and hacking. Advanced security technologies can help to prevent these attacks and protect users from financial losses.
- Build user trust and confidence. Security breaches can cause significant damage to a company’s reputation and erode user trust. Implementing robust security technologies can help to build user confidence in the app and increase customer loyalty.
- Regulatory compliance. Many countries have regulations that govern the use of mobile payment options and require specific security measures to be in place to protect user information. Implementing these security technologies can help to ensure regulatory compliance and avoid legal penalties.
- Enhanced user experience. Mobile devices that incorporate security technologies can provide users with a seamless and hassle-free experience. For example, biometric authentication can eliminate the need for complex passwords and make the payment process more convenient and faster.
In summary, the use of security technologies is essential for mobile payment apps to protect sensitive financial information, prevent fraud and cyberattacks, build user trust, ensure regulatory compliance, and provide a better user experience.
Security technologies in mobile payments
There are a number of security technologies commonly used in mobile payment applications. Among the most common are NFT, NFC, encryption, EMV, biometric authentication and tokenisation.

Point-to-point encryption
Point-to-point encryption (P2PE) – provided by a third party, P2PE combines security devices, processes, and applications to encrypt data until it reaches the solution provider’s secure environment for decryption. Because confidential cardholder data is instantaneously encrypted, customers are exposed to a considerably reduced risk of payment card fraud. For merchants who implemented this technology, it means that in the event of fraud, the P2PE solution provider not the merchant is held responsible for the data loss.
Tokenisation
Tokenisation – a security strategy that replaces sensitive data with a non-sensitive element, called a token, that has no exploitable value. Its core value is to replace a real card number with a surrogate, which subsequently reduces cybersecurity risks.
EMV
EMV – a global standard for cards equipped with the technology used to authenticate chip-card transactions, EMV stands for “Europay, MasterCard and Visa”. With the increased number of significant data breaches and cyber threats, more and more card issuers are opting for this technology to give their consumers peace of mind and reduce the risk of fraud.
NFC
NFC – near field communication, or NFC, is a wireless data transfer method that allows other devices within close proximity to exchange data without an internet connection. The technology is already being used for contactless credit card payments, but recently came back in the spotlight when it was introduced as a method of digitizing mobile payment software. In other words, NFC is a key pillar in the development of mobile wallets.
Biometric authentication
Biometric authentication is gaining popularity, as it provides a high level of security and convenience for users. However, it is important to note that biometric data is sensitive information and must be handled with care. To protect users’ privacy and prevent unauthorized access to their biometric data, mobile payment providers should implement robust security measures, such as encryption and secure storage of biometric data.
Biometric authentication involves using unique physical characteristics, such as your fingerprint or facial features, to verify your identity. This helps to ensure that only authorized users are able to access your mobile payment app and make transactions.
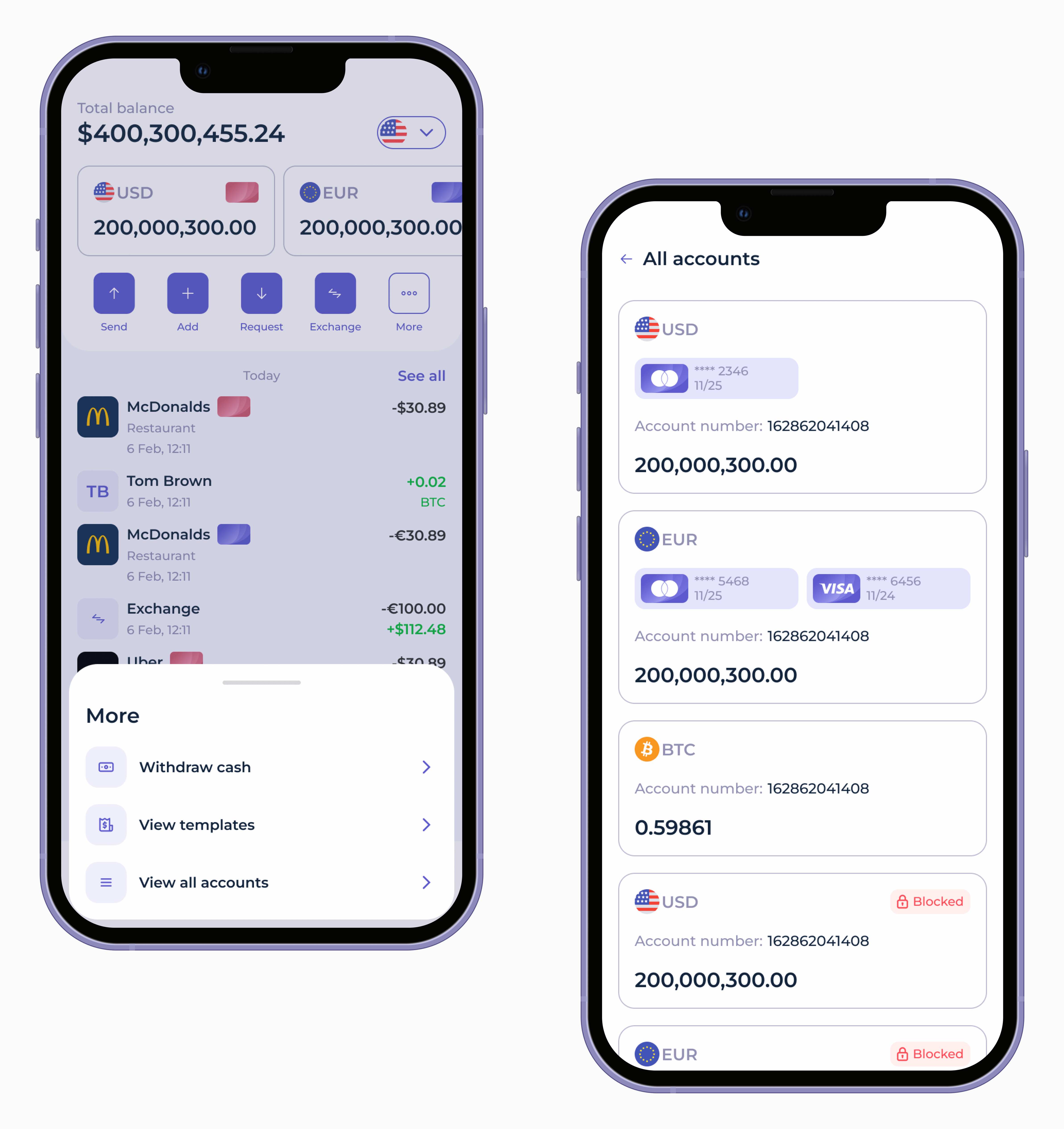
Having explored the crucial role of advanced security technologies in mobile payment applications, let’s now delve into a live demonstration of SDK.finance Mobile’s user interface. See firsthand how these security measures seamlessly integrate with a sleek and intuitive design, empowering users with both peace of mind and convenience in their mobile payment experiences:
Conclusion
Mobile payment apps offer a convenient and efficient way to pay for goods and services, but they also carry an increased risk of fraud and identity theft. For this reason, it’s important that mobile payment options are equipped with strong security technologies to protect your finances. Through the use of encryption, tokenization, biometric authentication and fraud detection, payment applications can help protect your financial data and keep your finances safe from cybercriminals. Whether you’re a consumer or a business owner, it’s important to be aware of the security risks and take steps to protect yourself and your customers.