Voice interaction is already speeding up daily banking tasks, from logging in and activating cards to making transfers and paying bills. Voice technology has the potential to improve financial services in more ways than just convenience and accessibility. New opportunities and cost savings that come from integrating voice interaction with digital touchpoints will be among the factors that separate leaders from followers in the decade to come.
Powered by advances in Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and neural language processing (NLP), voice assistants have become commonplace in cars, homes, and workplaces. Juniper Research estimates that over 4.2 billion digital voice assistants are in use on devices worldwide – a number that is projected to double by 2024. The rapidly growing market is an addressable opportunity for banks, payment providers, and other financial institutions.
What is voice banking?
Voice banking is a process that provides a person with voice management for all everyday banking operations.
The winners in this latest financial services frontier will be those that leverage modern technology to realize the potential of voice payments technology.
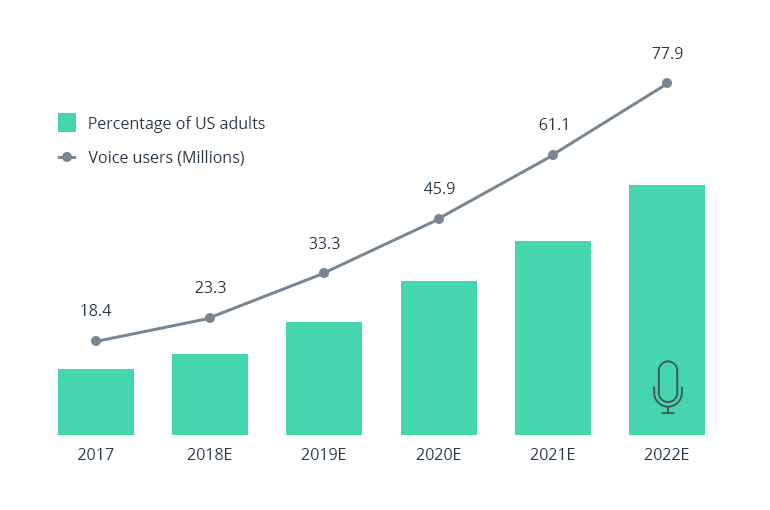
Voice payments adoption in the USA. Source: Business Insider – The Voice Payments Report 2017
Voice banking is evolving
The voice space is expected to become the next big platform for consumers and businesses to engage. Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and Apple are aggressively competing to capture and retain consumers within their ecosystems, accelerating innovation in areas like Conversational AI for Banks. The latest battleground centers around the smart speaker segment.

By early 2020, more than a third of U.S. adults owned a speaker with a voice assistant. The lockdown caused by the global pandemic has inadvertently caused a global boom in smart speaker purchases. According to experts, the coronavirus has accelerated the adoption of voice assistants by three to four years.
Mobile devices still form a significant part of the market. Out of consumers who use voice assistants, 81% do so via smartphones. 63% of owners of 2.5 billion active Android devices have used a virtual assistant, slightly behind the 75% of iPhone owners who have used Siri.

According to research, voice assistants are most commonly used in cars. More than half of the U.S. adult population spends 51 minutes in their cars every day. Similarly, European workers spent 84 minutes on average commuting in their car in 2018. Voice interaction is much safer and more convenient than typing, a strong argument for embracing the hands-free technology.
The majority of people rely on voice assistants to seek information and play music. The interesting part is that 28% of users have already made voice payments. 44% of questioned customers expressed interest in using voice assistants for routine bank operations, demonstrating an increase in interest towards voice banking.

Level of usage across a variety of functions
Source: Capgemini Digital Transformation Institute, Conversational Commerce Survey
Banks and financial institutions have responded to the demand by introducing voice payment functionality. The number of people who have tried paying by voice is expected to hit 45 million by the end of 2020, enabling customers to use their voice for balance checkup, transfers, credit, and bills payments.
Hybrid-cloud fintech platform
Save 1 year of active development building on SDK.finance software
More detailsOnce the technology is adopted, the potential for voice payments will be enormous. Roughly 80% of consumers already report satisfaction with the voice shopping experience.

Voice payments adoption in the USA. Source: Business Insider – The Voice Payments Report 2017
The main barrier to implementing voice payments lies in outdated core banking platforms that cannot facilitate new features. Smart assistants are increasingly becoming the differentiating feature that is helping challengers get a foothold in the market. Voice payment technology is transforming the FinTech industry and those that remain undecided risk falling behind.
ING was among the first banks to introduce a voice control function to its app back in 2014, which used Nuance’s voice-recognition software to launch Inge, the assistant. Customers could also find the nearest branch and pay their contacts. Other banks quickly followed suit. Some chose to launch their proprietary digital assistants and chatbots, while others integrated their services with Siri, Google, and Alexa.

Bank of America released their AI-empowered digital assistant called Erica in 2016 to facilitate voice payments. Eighteen months after launch, the platform attracted 10 million customers and handled 100 million requests from them. Erica can handle voice, text, and gesture commands to make transfers, list transactions, and provide guidance by analyzing consumer habits.
Erica has successfully helped Bank of America gain insights into what their customers want from a voice banking assistant. Simultaneously, they used the data gathered from voice requests to personalize their digital services and provide a better banking experience.
Capital One created a voice interaction service that uses Alexa to help consumers make credit card payments, check account balances, and get a snapshot of their spending habits. Barclays chose to integrate with Siri instead. The bank’s customers can pay existing payees or mobile contacts without opening the banking app or inputting passwords, immensely speeding pay simple transactions.
Venmo, Square Cash, and PayPal have also joined the ranks of financial companies that support voice payments.
Research by Strategy& shows that voice banking technology can be applied across both the front and back office to free up line branch staff, reduce call center call volume, and minimize operations. By addressing these key points, banks could gain 15% to 35% in efficiency across the value chain.

Check this article to get updated information about voice banking.
Voice banking can unlock large efficiencies
The convenience, security, and reach of the maturing technology are taking customer experience to a completely new level.
Greater convenience
Linking bank, debit, or credit card details with a personal voice assistant unlocks a whole new level of convenience. A driver behind the wheel, an athlete on the run, or a mother with her hands full can easily pay, subscribe, buy, reserve, and complete almost any transaction anywhere. Whether it’s a reservation that requires a deposit or a bill that’s coming up, a voice banking assistant can handle it. Fast, frictionless, and always available.
Lower systemic risk
Accounts are hacked and exploited every day. 81% of hacks leveraged stolen and weak passwords. Voice authentication is an opportunity to systematically improve customer security and, therefore, lower the chance of fraud and money laundering across the industry.
Broader reach
People with visual impairments make up another potential key segment. Blindness and vision impairment affect at least 2.2 billion people worldwide (28% of the world’s population). Voice banking would not only allow these people to manage their finances independently but eliminate the need to visit branches altogether.
Smarter communication
Voice banking can remove language barriers with live translations, dramatically increasing the number of people a bank or financial institution can service. In the U.S. alone, there are 67 million people who speak a language other than English. With voice banking, financial companies can expand their services across borders and gain millions of new customers.
In most cases, the main barrier to implementing new powerful voice features lies in outdated core banking platforms that cannot facilitate new features. Smart assistants are increasingly becoming the differentiating feature that is helping challengers get a foothold in the market.
However, FinTech companies have grown deeply concerned about the future of voice-based interfaces after hearing about Microsoft’s latest release of VALL-E. That’s why voice cloning technology enables the creation of counterfeit audio clips or voice commands that sound exactly like the original voice, raising many concerns about the potential misuse of this technology. Read our article to clarify why voice cloning technology can be dangerous for FinTech industry.
Conclusion
The adoption of voice technology has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry. With over 4.2 billion digital voice assistants projected to be in use by 2024, voice interaction has become a commonplace feature in cars, homes, and workplaces. As banks and financial institutions seek to leverage the latest technology to improve their services, voice banking has emerged as a promising area of growth. Voice assistants can help customers manage their everyday banking operations, from making transfers to paying bills, and more.


