In 2024, financial regulators issued over $4.3 billion in penalties worldwide, with US regulators alone accounting for 95% of these enforcement actions. The sharpening focus on anti-money laundering (AML) compliance has resulted in several notable penalties, including a staggering $3.1 billion penalty against TD Bank for AML violations. This punitive regulatory landscape underscores a crucial truth for financial institutions: compliance is no longer optional, it’s existential.
At the heart of financial compliance sits an often-overlooked yet foundational component: the Transaction Processing System (TPS). While typically viewed through the lens of operational efficiency, a robust TPS serves as the bedrock for regulatory compliance, audit readiness, and comprehensive financial integrity.
This article examines how a well-structured TPS contributes to payment compliance, supports financial audits, and streamlines regulatory reporting, positioning it not merely as a transaction handler but as a critical compliance enabler for financial institutions navigating an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Why Compliance Is a Growing Priority for FinTechs
The regulatory landscape for financial institutions continues to evolve at a rapid pace, creating significant challenges for FinTechs that must adapt quickly to remain compliant. Several key regulatory drivers are reshaping the compliance landscape:
Tightening AML Regulations
The implementation of the 6th EU Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD6) represents a significant shift in compliance requirements. Unlike previous directives, AMLD6 introduces criminal liability for AML failures, harmonises the definition of money laundering offences across the EU, and extends liability to legal entities in addition to individuals.
For FinTech companies, this means implementing more robust AML frameworks that can identify suspicious transactions with greater precision.
“Based on SDK.finance’s experience with financial institutions across Europe, we’ve observed that companies implementing proactive transaction monitoring strategies ahead of AMLD6 deadlines have experienced fewer regulatory enquiries compared to those taking a reactive approach,” notes Alex Malyshev, CEO of SDK.finance. “The shift from entity-based to activity-based monitoring has proven particularly effective in identifying suspicious patterns that traditional KYC processes might miss.”
Increasing Regulatory Scrutiny
Regulatory bodies worldwide are intensifying their oversight of financial institutions, with particular attention to emerging FinTech companies. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) continues to update its recommendations, requiring more sophisticated monitoring and reporting mechanisms for suspicious activities.
Rising Compliance Costs
According to recent industry analyses, financial crime compliance costs are projected to exceed $22 billion by mid-2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 23.5%. This rapid increase reflects the expanding scope and complexity of compliance requirements that financial institutions must address.
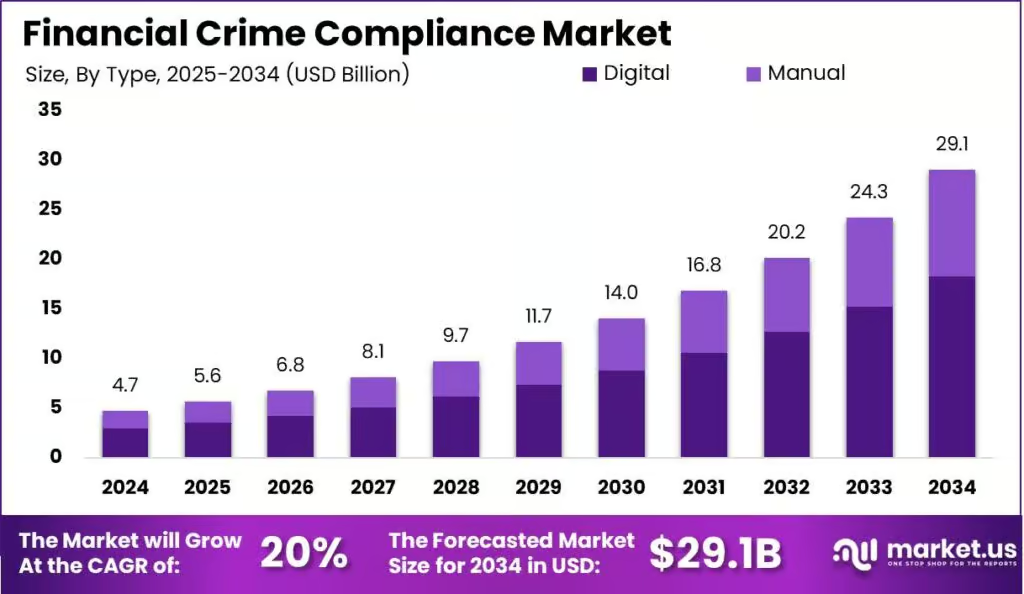
Source: Market.us
Costly Consequences of Non-Compliance
Beyond the immediate financial penalties, non-compliance carries significant reputational damage and potential loss of banking relationships. For payment service providers (PSPs) and e-money institutions (EMIs), these consequences can be particularly severe, potentially leading to license revocation and business closure.
In this environment, having systems that can adapt to changing compliance requirements is not just a regulatory necessity but a business imperative. This is where a well-structured Transaction Processing System becomes invaluable.
Discover how the SDK.finance TPS can power high-speed, secure operations across banking, fintech, and retail
ExploreTPS as the Backbone of Financial Data Integrity
Transaction Processing Systems serve as the central nervous system for financial operations, ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and traceability of all financial data flowing through an organisation. This role is essential not only for operational efficiency but also for maintaining financial data integrity, a cornerstone of compliance and audit readiness.
Ensuring Transaction Traceability
A robust TPS creates a comprehensive audit trail by capturing detailed information for every transaction:
- Transaction initiator identification
- Timestamp information (creation, modification, approval times)
- Source and destination account details
- Transaction type classification
- Amount and currency information
- Reference data and transaction purpose
This level of detail ensures that auditors and compliance officers can trace the complete lifecycle of any transaction, from initiation to settlement, providing crucial visibility for regulatory review.
Creating Tamper-Proof Records
Modern TPS implementations incorporate safeguards against unauthorised modifications:
- Record-level locking mechanisms
- Digital signatures for transaction validation
- Hash-based data verification
- Role-based access controls
- Automated logging of all access attempts
These features create a secure transaction environment where alterations are virtually impossible without detection, addressing a key requirement for financial regulators concerned with fraud prevention and data integrity.
Establishing Consistent Data Structure
A well-designed TPS enforces consistent data standards across all transactions, which is invaluable for compliance purposes:
- Standardised transaction codes and categories
- Uniform data field requirements
- Consistent formatting of monetary values
- Structured payment reference information
- Normalised customer identification data
This consistency simplifies regulatory reporting by ensuring that data can be reliably aggregated and analysed according to regulatory requirements.
Discover how the SDK.finance TPS can power high-speed, secure operations across banking, fintech, and retail
ExploreStrengthening AML and KYC with Transaction Data
Real-time Fraud Pattern Recognition
Modern Transaction Processing Systems have evolved beyond simple record-keeping to incorporate sophisticated pattern recognition capabilities:
- Unusual transaction timing detection
- Identification of atypical transaction amounts
- Recognition of suspicious transaction sequences
- Detection of unusual geographic patterns
- Flagging of transactions with sanctioned entities or high-risk jurisdictions
These capabilities help financial institutions detect potentially fraudulent activities as they occur, rather than discovering them during periodic reviews when damage may already be done.
Linking Identity Verification to Transaction Trails
A TPS serves as the critical connection point between KYC procedures and ongoing transaction monitoring:
- Verification of transaction parties against KYC records
- Automatic flagging of transactions involving unverified or partially-verified entities
- Integration with identity verification workflows
- Risk-based transaction restrictions tied to KYC status
- Documentation of the relationship between transaction parties
This integration ensures that transactions only proceed with properly identified parties, addressing a core requirement of AML regulations worldwide.
Supporting Ongoing Due Diligence with Behavioural Data
“Based on SDK.finance’s experience with real-time processing platforms, behavioural transaction data is a critical layer in modern AML systems. The patterns in how customers transact often reveal compliance risks that static KYC data alone could never identify,” notes industry experts.
A comprehensive TPS captures rich behavioural data that supports ongoing due diligence:
- Transaction frequency analysis
- Typical transaction amount profiles
- Common transaction counterparties
- Usual geographic transaction patterns
- Time-of-day transaction tendencies
These behavioural profiles allow compliance officers to spot anomalies that may indicate suspicious activity requiring further investigation.
Enabling Transparent Audit Trails
For financial auditors, a well-implemented TPS provides the transparency and traceability needed to verify financial integrity. This transparency comes through several key capabilities:
Comprehensive Action Logging
A robust TPS maintains detailed logs of all system interactions:
- User access events (login/logout activities)
- Transaction creation and modification events
- Approval and authorisation actions
- Configuration changes affecting transaction rules
- System-generated notifications and alerts
This comprehensive logging ensures that auditors can reconstruct the complete sequence of events surrounding any transaction.
Immutable Audit Histories
Modern Transaction Processing Systems increasingly implement immutable record-keeping approaches:
- Sequential transaction numbering
- Cryptographic chaining of transaction records
- Timestamp verification mechanisms
- Blockchain-inspired distributed ledger capabilities
- Digital notarisation of transaction batches
These approaches make it technically impossible to alter historical records without detection, providing auditors with confidence in the integrity of the financial data being examined.
Role-Based Access Controls with Documentation
Transaction systems with strong compliance features implement detailed access controls:
- Granular permission structures by transaction type
- Four-eyes principle enforcement for sensitive operations
- Documented approval workflows
- Segregation of duties enforcement
- Automatic notification of security exceptions
These controls help auditors verify that appropriate governance was in place for all financial activities and that transactions were properly authorised according to organisational policies.
Time-Based Data Retention
Compliant TPS implementations include sophisticated data retention capabilities:
- Automatic archiving of transaction data based on age
- Retention period enforcement aligned with regulatory requirements
- Secure, read-only access to archived transactions
- Legal hold mechanisms for transactions under investigation
- Compliant data destruction protocols
These features ensure that transaction records remain available for the legally required retention periods while supporting proper data lifecycle management.
Supporting Regulatory Reporting at Scale
Generating Custom and Standardised Reports
A compliance-oriented TPS provides robust reporting capabilities essential for regulatory submissions:
- Configurable reporting templates aligned with regulatory formats
- Parameter-driven report generation
- Cross-functional data aggregation
- Exception highlighting and flagging
- Historical comparison capabilities
These features allow financial institutions to efficiently produce the documentation required for regulatory oversight without time-consuming manual data compilation.
Automating Data Exports for Regulators
Modern TPS platforms streamline the regulatory reporting process through automation:
- Scheduled report generation
- Direct secure transmission to regulatory portals
- Format validation prior to submission
- Automated reconciliation of reported figures
- Audit trails of regulatory submissions
This automation reduces both the resource burden and the risk of errors in regulatory reporting, a critical consideration given the penalties associated with inaccurate submissions.
Integrating with Analytics Tools via APIs
Leading Transaction Processing Systems offer extensive integration capabilities:
- RESTful APIs for data access
- Real-time data streaming for analytics platforms
- Batch export facilities for data warehousing
- Secure data sharing mechanisms
- Custom webhook implementation for event-driven reporting
These integration points allow financial institutions to leverage specialised compliance and analytics tools while maintaining the TPS as the authoritative system of record.
Discover how the SDK.finance TPS can power high-speed, secure operations across banking, fintech, and retail
ExploreSDK.finance’s Compliance-Ready TPS
SDK.finance has developed a Transaction Processing System specifically designed to address the compliance needs of modern financial institutions. Key features include:
Comprehensive Audit Trail Implementation
The SDK.finance platform captures detailed metadata for every transaction, including:
- Originator information
- IP address and device fingerprinting
- Location data when available
- Complete timestamp information
- Session context and referral path
This detailed audit trail provides compliance officers with the context needed to properly evaluate transaction patterns and respond to regulatory inquiries.
Role-Based Access with Granular Controls
The platform implements sophisticated access controls:
- Multi-level approval workflows
- Division of responsibility enforcement
- Temporary access provisioning with automatic expiration
- Detailed permission audit logs
- Support for regulatory segregation requirements
These controls ensure that only authorised personnel can perform sensitive operations, with all access fully documented for audit purposes.
Accountant Dashboards and Transaction Tagging
Purpose-built interfaces for compliance and accounting staff include:
- Custom tagging capabilities for transactions requiring attention
- Risk scoring visualisation
- Trend analysis tools
- Exception dashboards
- Customisable alert thresholds
These features allow compliance teams to efficiently monitor transaction activity and focus attention on high-risk areas.
Regulatory Reporting Templates
The platform includes pre-configured templates for common regulatory requirements:
- Suspicious transaction reporting formats
- Large transaction reporting
- Cross-border transfer documentation
- Currency transaction reporting
- Periodic regulatory submissions
These templates significantly reduce the effort required to maintain regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
Conclusion
As regulatory pressures intensify and compliance costs continue to rise, financial institutions must recognise that their Transaction Processing Systems represent far more than operational infrastructure. They are critical compliance assets that can either facilitate or hinder regulatory adherence.
A well-designed TPS provides the foundation for effective compliance through:
- Comprehensive transaction traceability
- Immutable audit trails
- Real-time monitoring capabilities
- Efficient regulatory reporting
- Integrated KYC/AML functionality
By investing in a robust Transaction Processing System with strong compliance features, financial institutions can transform what might otherwise be a burdensome regulatory obligation into a strategic advantage, reducing compliance costs, minimising regulatory risk, and building customer trust through demonstrable financial integrity.
For FinTechs seeking to navigate the complex compliance landscape efficiently, evaluating your Transaction Processing System through the lens of compliance capability is no longer optional. It’s essential for sustainable operation in today’s highly regulated financial environment.
To learn more about how SDK.finance’s Transaction Processing System can support your compliance objectives, contact our team for a consultation tailored to your specific regulatory requirements and business model.
Discover how the SDK.finance TPS can power high-speed, secure operations across banking, fintech, and retail
Explore