From restaurant menus to event tickets, QR code payments have become a go-to solution for businesses worldwide, with companies like Starbucks and Walmart leading the charge. For banks and FinTechs, this surge presents a golden opportunity to enhance customer engagement, offering faster, secure, and touch-free transactions.
But how exactly are QR codes transforming the customer experience, and what does this mean for the future of payments? Let’s dive in.
From scan to sale: The QR code revolution in payments
The QR code revolution is transforming the way we shop, dine, and do business, offering lower transaction fees, faster processing times, and easier adoption for businesses of all sizes. This rapid shift toward payment with QR codes isn’t just a passing trend—it’s a global movement that’s reshaping the entire payment industry.
The numbers speak for themselves: the global QR code payment market was worth $9.98 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow by 16.9% each year from 2023 to 2030.
Market size of QR code transactions with forecasts from 2021 to 2025
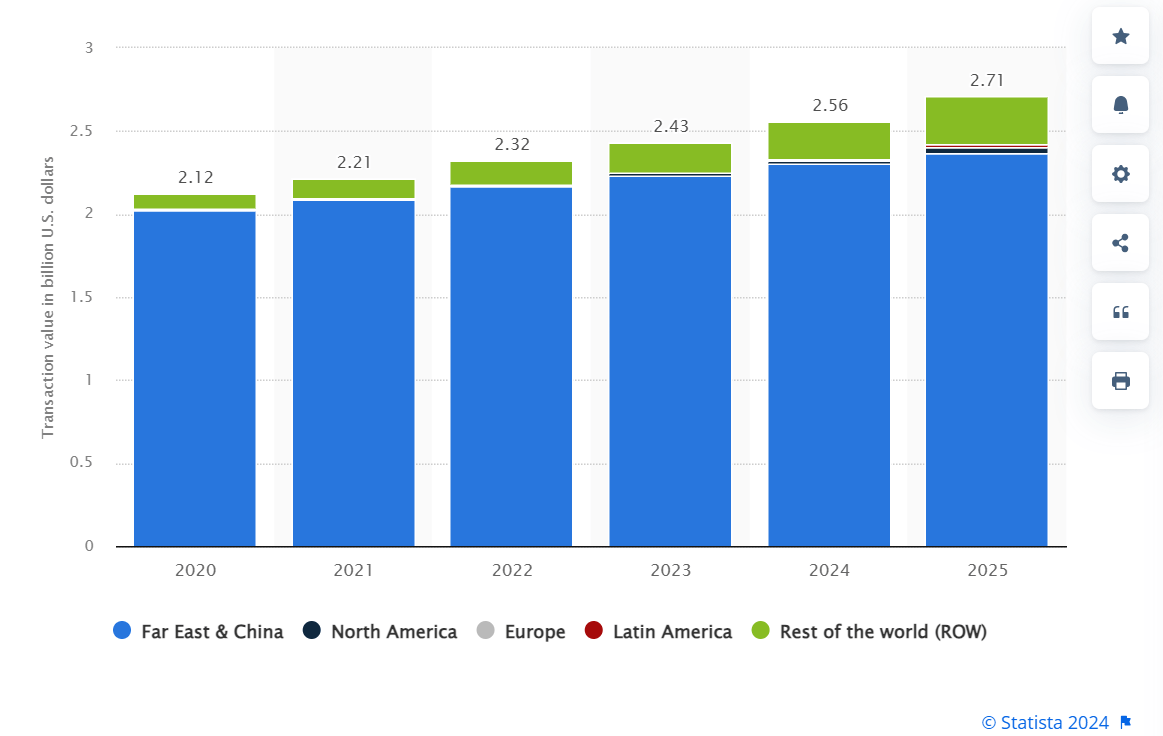
Source: Statista
According to Statista, in 2020, the global QR code payment market saw significant growth, especially in regions like China, India, and Southeast Asia, where mobile wallets dominated transactions.
By 2025, the market is expected to continue expanding rapidly, driven by increasing smartphone penetration and rising demand for contactless payments. Forecasts indicate steady growth in the U.S. and Europe as well, as payment with QR codes become more integrated with faster payment systems and open banking solutions.
But the real question is: what makes this technology so appealing? From lowering transaction fees to speeding up processing times, the benefits of QR code payments are clear for both businesses and consumers alike. Let’s break down the key advantages.
Benefits of QR code payments
Low cost
QR code payments offer a cost-effective solution for both businesses and consumers compared to traditional payment methods like credit card terminals. Businesses can implement QR code systems without needing expensive hardware, leading to lower transaction fees and infrastructure costs.
The low implementation cost of QR code payments has significantly contributed to their popularity among small Southeast Asian merchants. Countries like Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia have seen a surge in mobile wallets such as GrabPay, GCash, and Alipay, where customers can simply scan a QR code to complete transactions.
High speed
QR code payments enable real-time or near-instant settlement, which aligns with the growing demand for faster payments. By facilitating quick payments without waiting for card authentication or approval, QR code systems can reduce checkout times, benefiting both merchants and consumers, particularly in high-traffic environments like retail stores or restaurants.
The rapid adoption of QR code payments in China has revolutionized the retail and transportation sectors. Platforms like WeChat Pay and Alipay enable users to complete transactions in seconds, making them the preferred payment methods for everyday purchases.

Source: Sandy.land
Fostering faster payment adoption
In countries like the UK, QR codes have been integrated with faster payment networks, making it easier for businesses and consumers to adopt. For example, account-to-account (A2A) payments, which bypass card networks, are growing in popularity due to their speed and lower fees.
The UK’s robust faster payment infrastructure has enabled widespread QR code adoption, providing an alternative to traditional card networks through direct and efficient bank transfers.
Account-to-account payments
QR codes are particularly well-suited for account-to-account (A2A) payments, where users can transfer funds directly from their bank account to a merchant or another individual without involving intermediaries like card networks.
A2A payments using QR codes are already popular in countries like India (Unified Payments Interface) and Brazil (PIX), where they have streamlined money transfers by eliminating middlemen. Pay by scanning QR code offers faster settlement, lower fees, and increased transparency for both consumers and businesses, contributing to the overall appeal of QR code payments.
However, implementing QR code payments can face several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful adoption.
Everything you need to launch crypto wallets, payments, and custody
Learn moreChallenges of QR code payments implementation
Fragmented payment landscape
One significant challenge is the fragmented payment landscape in markets like the U.S., where multiple payment networks and systems coexist without a unified QR code standard. This fragmentation can lead to confusion for consumers and merchants alike, making it difficult to create a seamless payment experience.
Security concerns
Another challenge is the need for robust security measures to protect against fraud. As QR codes often link to URLs, they can be susceptible to malicious attacks if not properly secured. The development of dynamic QR codes and encryption standards, such as those proposed by ANSI X.9, is crucial to addressing these security concerns.
Technical integration
Lastly, the integration of QR code payments into existing systems can present technical hurdles. Merchants may need to update their payment infrastructure and train staff, which can incur additional costs. This is particularly relevant in environments with multiple payment terminals, where adding a QR code scanner might complicate the checkout process. Overcoming these challenges is essential for realizing the full potential of QR code payments in the U.S. market.
However, Platforms like SDK.finance offer a ready-made solution, providing flexible payment infrastructure that seamlessly integrates QR code payments into existing systems with minimal friction. SDK.finance’s robust API and open banking integrations help businesses navigate technical challenges, making the adoption of QR code payments faster and easier.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for ensuring the widespread adoption of QR code payments. However, addressing the technical and security concerns isn’t enough—regulation also plays a critical role.
Regulation for QR code payments
UK
The UK has a well-structured regulatory framework for QR code payments, overseen by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Payment Systems Regulator (PSR). QR codes are integrated into the UK’s Faster Payments system, enabling quick, account-to-account (A2A) transfers.
These regulations ensure security through strict anti-fraud measures and initiatives like Open Banking support easy interoperability between banks and fintechs. This regulatory backing has been a key driver of QR code adoption in the UK, especially for faster payments.
USA
In the U.S., QR code payments face a slower adoption curve due to a fragmented payment system and the lack of a universal QR code standard. Unlike the UK, the U.S. doesn’t have comprehensive regulatory oversight for QR code payments, which has hampered growth.
However, the Federal Reserve’s new real-time payment platform, FedNow, could lay the groundwork for QR code payments in the future. Strong regulations around data security, consumer protection, and standardization will be critical to speeding up adoption in the U.S.
Europe
Across Europe, QR code payments are gaining momentum, thanks to regulations like the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2). PSD2 has paved the way for Open Banking, allowing secure and easy account-to-account transfers across borders.
The European Central Bank (ECB) is also encouraging instant payments, which aligns with the growing use of QR codes. While EU countries share a common regulatory approach, each nation still has its own regulatory bodies overseeing local payment systems.
Other regions
In Southeast Asia, countries like Singapore, Indonesia, and Malaysia have been at the forefront of QR code payment adoption, supported by government-backed standards like Singapore’s SGQR. These centralized systems make QR code payments highly interoperable, helping them become the go-to payment method in many countries.
China and India are other success stories, where government regulation has ensured security and streamlined payments. India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), for example, provides a standardized, secure platform for QR code payments.
Globally, the key to successful QR code payment regulation lies in balancing innovation with security, fostering interoperability, and building consumer trust through robust regulatory frameworks.
Use Case: Open banking payments on a payment terminal link
Integrated with QR code technology, open banking payments are transforming how consumers and merchants conduct transactions. When purchasing, instead of relying on traditional card networks, customers can initiate payments directly from their bank accounts using open banking APIs.
This method allows for real-time account-to-account (A2A) payments, bypassing the need for credit or debit cards. Customers enjoy faster, more secure transactions, while merchants benefit from lower transaction fees since payments don’t go through traditional card networks.
For businesses, this means quicker settlement times and the ability to offer more flexible payment options. It’s a powerful alternative to card payments, particularly in countries with advanced Open Banking systems.
For example, Barclays’ “Pay by Bank” app allows consumers to make purchases directly from their bank accounts using open banking APIs without needing a card. When shopping in-store or online, the customer selects “Pay by Bank” at checkout, and the merchant’s payment terminal generates a QR code.
SDK.finance Platform supports open banking payments, allowing businesses to integrate account-to-account (A2A) transactions with QR code technology. This means customers can pay directly from their bank accounts via QR codes, offering a streamlined, secure, and fast payment option for both merchants and consumers.
Wrapping up
QR code payments are revolutionizing the way we shop and interact with businesses, offering benefits like lower transaction fees, faster settlement times, and seamless integration with open banking systems.
While challenges such as a fragmented payment landscape, security concerns, and technical integration remain, Platforms like SDK.finance can help businesses implement these solutions efficiently.




