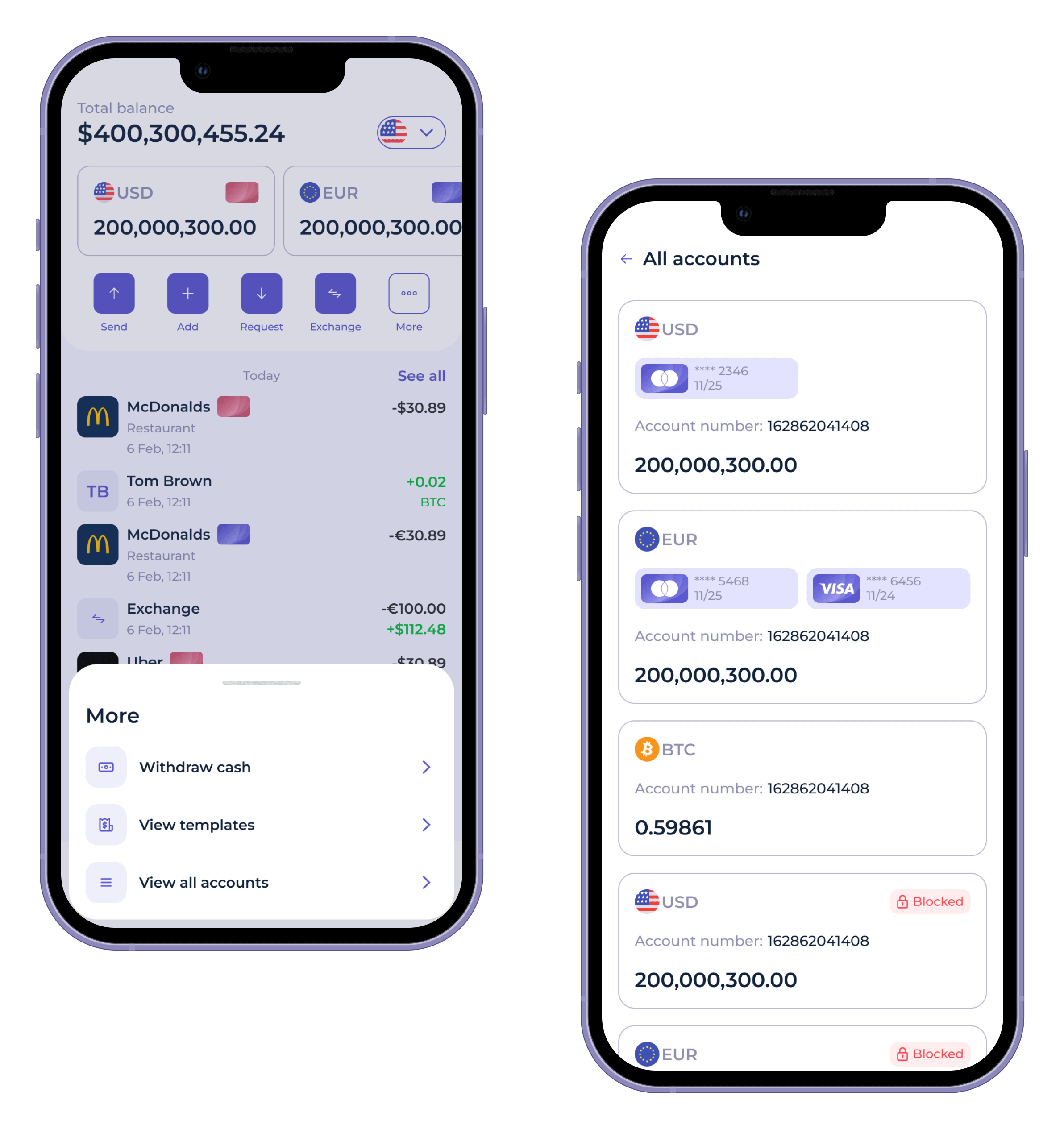
As customers demand more control and autonomy over their finances, and in view of the pandemic that locked so many of us inside, banks are now introducing more customer-friendly core banking solutions to boost customer satisfaction and win more loyal customers. Companies like Oracle and IBM have also introduced automation and advanced data processing to fine-tune operations and increase their knowledge base.
More and more often, fintechs that strive to keep pace with fast-evolving market are investigating what is core system in banking going to provide them in case it is implemented – and whether it’s worth the effort.
So, if you are pondering whether to adopt a core banking solution, let us explore the concept and importance of a core banking system in details. Read on to discover core banking advantages and disadvantages.
What is core banking?
Core banking is a back-end system that connects multiple branches of the same bank together to deliver operations like loan management, withdrawals, deposits, daily banking transactions, and payments in real time.
What does core banking mean?
The term CORE stands for Centralized Online Real-time Environment, which implies that the customer can experience the bank as a single entity, regardless of their location – with the aim to provide more independence for the customers in terms of using their accounts and conducting transactions from any location in the world.
Core banking applications are designed to provide seamless integration and advanced tools for compliance and innovation across different banking sectors.
What are IT core banking services?
The key core banking services, which are integral to the banking infrastructure, include new account creation, account management, customer relationship management, interest calculations, deposits and withdrawals processing, loan issuing and servicing etc.
How does core banking work?
A core banking system comprises back-end servers that handle standard operations, processes daily banking transactions like interest calculation, passbook maintenance, and withdrawal, forming the backbone of the banking infrastructure.
When a customer withdraws money from a branch or an ATM, the application sends a request to the centralized data center, which then processes the request and authenticates the operation.

Source: Bangaloreicai.org
The data center contains the database, an application server, a web server, and a firewall to protect the system from malware attacks. Banks can host their data center locally or on the cloud.
Core Banking System Architecture
A core banking system architecture is designed to provide a scalable, secure, and efficient platform for managing daily banking transactions. The architecture typically consists of several layers, each playing a crucial role in the system’s overall functionality:
- Presentation Layer: This layer serves as the user interface, allowing customers and bank employees to interact with the core banking system. It includes web and mobile interfaces that facilitate account management, transaction processing, and customer support.
- Application Layer: This layer handles the business logic of the core banking system. It manages essential functions such as account management, loan management, and customer relationship management. By processing these operations, the application layer ensures that the core banking system can meet the diverse needs of financial institutions.
- Data Access Layer: This layer provides access to the core banking system’s database. It acts as a bridge between the application layer and the database, ensuring that data is retrieved and stored efficiently. This layer is critical for maintaining the integrity and consistency of customer information, account data, and transaction history.
- Database Layer: This layer is responsible for the storage and retrieval of data within the core banking system. It manages the database where all customer information, account details, and transaction records are kept. A robust database layer is essential for ensuring data security and quick access to information.
- Infrastructure Layer: This layer provides the underlying infrastructure for the core banking system, including servers, storage, and network connectivity. It ensures that the system is scalable and can handle the increasing volume of daily banking transactions. Additionally, it supports the operational efficiency and security of the entire core banking platform.
A well-designed core banking system architecture is essential for ensuring operational efficiency, scalability, and security. By integrating these layers effectively, financial institutions can provide reliable and efficient banking services to their customers.
Core banking software market size
The global core banking software market was valued at USD 10.89 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.3% from 2023 to 2030.
Financial institutions are increasingly launching new business models to enhance competitiveness and meet evolving customer expectations within the rapidly changing financial landscape. The rise of the market is due to the increasing integration of technology for basic banking transactions and services.

As the core banking landscape evolves with these prominent trends, the market is poised for significant growth. The increasing adoption of digital transformation, cloud solutions, open banking practices and cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain are collectively contributing to the expansion of the global core banking software market.
Below, we delve into the statistics surrounding the global core banking market share:

Broken down by bank type, the market comprises small banks, mid-sized banks and community banks and credit unions. Large banks are expected to dominate the market share for core banking software during the forecast period.
What are the essential IT core banking features?
After analyzing the top core banking software vendors, we’ve figured out the core banking features indispensable in a decent solution that supports a robust banking infrastructure.
- Centralized dashboard
Bankers need a single-view dashboard to visualize the system in real-time. Also, bankers and clients should have access to the same dashboard view; this will help diagnose and solve issues faster.
- Onboarding (with KYC features)
Before using the dashboard, the client must sign in to their account with a unique username and password. With KYC features, banks can verify the identities of prospective customers when they register. The onboarding process should also be simple enough for users to complete without stress.
Watch SDK.finance Platform’s demo video to explore how to manage your users, ensure KYC compliance, and prevent fraud with the robust system back office. This video showcases real-life scenarios demonstrating the power of the Clients section:
- Two-factor authentication
The solution needs to offer two-factor verification to boost security and protect clients’ sensitive data.
- Push notifications
When building a core banking solution for mobile, use push notifications to deliver timely account updates to clients.
- Loan management
The core banking solution must allow customers to monitor their loans and schedule payments according to the specified plan.
- Interest calculators
For loan and mortgage payments, users need access to real-time calculators to help them make informed decisions.
- Live chat
A live chat feature must be on the platform to help users contact support agents when they need assistance. Automated chatbots can also provide templated answers to frequently asked questions.
- Transaction management
Clients can customize their popular payments and P2P transfers to ensure that their contact lists remain updated. They can also use multi-currency exchanges to trade on their preferred currencies.
- Reporting tools
Effective banking software integrates various reporting tools crucial for financial management and analytics.
View the demo video of the SDK.finance Platform to see how you can streamline transaction management and guarantee financial compliance using our robust FinTech Platform:
What are the types of core banking systems?
Depending on the hosting, IT core banking systems can fall into the following categories, each leveraging different banking technology approaches:
- On-premise solution. This system works on a locally-hosted infrastructure, providing the bank administration with several customization options.
- Cloud-based core banking software – as the name suggests, it is hosted on the cloud. Sometimes, a cloud vendor offers the application as a Cloud as a Service (CaaS) on a pay-per-use basis. Other times, companies can move their local servers to the cloud to enjoy more flexibility.
Choosing the right core banking providers is crucial for ensuring seamless integration into existing platforms and staying competitive in the rapidly evolving banking sector. Read this article to explore the world of open source banking software.
What are the core banking system advantages?
With a better understanding of the working principle and features of the core banking platforms, let’s explore their key benefits:
-
Enhanced productivity
Core banking platforms increase operational efficiency by reducing the time it takes to connect with multiple branches. As a result, banks can process transactions faster, regardless of the client’s physical location.
-
Improved security
Core banking systems use advanced encryption modules to protect the infrastructure from hackers and malware. On the client’s side, bio-verification and two-factor authentication also provide additional layers of security to the platform. These features help banks maintain KYC standards and comply with other banking regulations.
-
24/7 access to banking services
In this era of contactless payments, access to round-the-clock bank services is vital. Users can conduct financial operations anywhere and anytime since the core banking platform never goes offline. Clients can also contact customer support for assistance at any time.
-
Lower operational costs
Banks can rely on their core platforms to reduce operational costs since these systems require fewer human resources to function. Besides, the AI-powered infrastructure increases the completion rate of operations and reduces the chances of errors in documentation.
-
Multiple currencies
Users can trade in multiple currencies instantly without needing to change large amounts at a currency exchange.
Leading financial institutions partner with providers like SDK.finance, which offers a broad range of financial software solutions to enable quick implementation of new functionalities with reduced risk.
Core Banking Work and Implementation
Implementing a core banking system requires meticulous planning, execution, and testing. The implementation process typically involves the following steps:
- Requirements Gathering: The first step is to identify the business requirements of the financial institution. This involves understanding the specific needs and defining the scope of the core banking system implementation. Clear requirements help in designing a system that aligns with the institution’s goals.
- System Design: In this phase, the core banking system architecture is designed, and the technical requirements for the implementation are defined. This includes outlining the structure of the application layer, data access layer, and database layer to ensure seamless integration and functionality.
- Software Development: This step involves developing the core banking software. It includes coding the application layer, data access layer, and database layer. The development process focuses on creating a robust and scalable system that can handle the institution’s daily banking transactions.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Before deployment, the core banking system undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets the business requirements and is free from defects. This phase includes functional testing, performance testing, and security testing to guarantee the system’s reliability and efficiency.
- Deployment: Once the system passes all tests, it is deployed in a production environment. This involves configuring the core banking system for use by bank employees and customers. Proper deployment ensures that the system operates smoothly and efficiently from day one.
- Training and Support: After deployment, training and support are provided to bank employees and customers. This ensures that all users are familiar with the core banking system and can utilize its features effectively. Ongoing support helps in addressing any issues that may arise post-implementation.
A successful core banking system implementation requires careful planning, execution, and testing to ensure that the system meets the business requirements of the financial institution. By following these steps, banks can deploy a reliable and efficient core banking platform that enhances their operational capabilities.
Limitations of IT core banking solutions
Despite the amazing benefits of core banking solutions, these systems still have flaws.
- Technical downtimes can disrupt regular banking operations, thereby frustrating clients. Retail banking services, in particular, can be significantly disrupted by technical downtimes, affecting customer satisfaction.
- Using a core banking system can introduce a single point of failure that affects all branches simultaneously in the case of a cyberattack.
- Modern core banking systems can be expensive to buy and maintain, especially for small and medium-sized banks.
- Legacy core banking software can leave the entire infrastructure vulnerable to system failure. The modernization effort will also cost a lot of money.
Legacy Core Systems vs. Next-Generation Systems
Legacy core systems are typically monolithic, meaning that all components are intertwined, making it difficult to make changes or updates. They often run on outdated technology stacks, requiring specialized skills to maintain. In contrast, next-generation core systems use an open, modular architecture, where components are decoupled and can run independently on different servers or in the cloud. This allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and innovation. Modern core banking systems enable financial institutions to quickly adopt to market changes, integrate new technologies, and offer enhanced services to their customers.
The Role of Core Banking in Banking Solutions
Core banking plays a pivotal role in modern banking solutions by providing a comprehensive platform for managing daily banking transactions. Core banking systems enable financial institutions to:
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Core banking systems automate many banking processes, reducing the need for manual intervention. This automation streamlines operations, allowing banks to process transactions more quickly and accurately. As a result, banks can achieve higher levels of operational efficiency.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Core banking systems provide a platform for delivering online banking services. Customers can manage their accounts, conduct transactions, and access banking services remotely. This convenience enhances the overall customer experience, making banking more accessible and user-friendly.
- Increase Revenue: By leveraging core banking systems, financial institutions can offer new banking services and products. These systems support the development and deployment of innovative financial products, helping banks attract new customers and increase revenue. Additionally, core banking platforms enable banks to adapt to changing market demands swiftly.
- Reduce Risk: Core banking systems provide a secure platform for managing daily banking transactions. Advanced security features, such as encryption and two-factor authentication, protect sensitive data from breaches and cyber attacks. By reducing the risk of data breaches, core banking systems help financial institutions maintain trust and compliance with regulatory standards.
In summary, core banking systems are a critical component of banking solutions. They enable financial institutions to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, increase revenue, and reduce risk. By adopting modern core banking platforms, banks can stay competitive in today’s digital age and meet the evolving needs of their customers.
Why choose a core banking solution?
Despite the few limitations mentioned earlier, your bank still needs a core banking platform to streamline banking operations and maximize ROI. A significant portion of retail banks worldwide have adopted cloud technology to various extents, despite ongoing challenges related to data security and regulatory risks.
When choosing a core banking provider, financial institutions should consider several key factors, including scalability, security, integration, customization, and support. They should also consider the provider’s experience, reputation, and ability to deliver a modern, flexible, and scalable core banking platform. Additionally, they should evaluate the provider’s ability to integrate with other systems and applications, and their commitment to innovation and customer experience. By modernizing their core banking systems and choosing the right core banking provider, financial institutions can improve their efficiency, effectiveness, and customer experience, and stay competitive in today’s digital age.
SDK.finance can help you develop banking software using a ready-made backend FinTech Platform to accelerate time to market. We provide a flexible banking core that serves as a foundation for building any PayTech products.
Our FinTechTech solution is a flexible core banking system designed to serve as a solid foundation for a wide range of PayTech products. The Platform supports various financial services, including digital wallets, money transfers, currency exchange, and payment acceptance, while ensuring high standards of security and compliance.
With built-in integrations and comprehensive back-office tools, SDK.finance simplifies the management of clients, transactions, and financial operations, allowing you to focus on innovation and growth.
Choose your development approach:
- Dedicated development team with more than 10 years of experience to bring your digital bank to life faster
- Self-service development with a pre-developed Platform by SDK.finance to support your technical team. The Platform is available as a cloud-based software by subscription and Source Code modes.
Both modes allow you to accelerate the development of your banking software and focus on the customer and product experience.
Watch SDK.finance Platform demo video to explore how our solution can empower you to build secure and feature-rich financial products 70% faster:
Final words
Core banking financial services offer several advantages to banks and their customers. With advanced data analytics, bank administrators can improve ROI while maintaining client satisfaction at an optimum level. You can also rely on automation to keep your application’s infrastructure running. Most importantly, modern core banking solutions will protect your company’s and client’s data from hackers.